A Unidirectional ring topology is thus easy to maintain compared to the bidirectional ring topology. Ex: SONET network, SDH network etc. A SONET/ SDH is a standardized network protocol that transfers data streams over optical fibers. Whereas, a bidirectional ring topology handles data traffic in both the direction and can be a full-duplex network. Topology rules allow you to define those relationships between features in a single feature class or subtype or between two feature classes or subtypes. Topology rules allow you to define the spatial relationships that meet the needs of your data model. Topology errors are violations of the rules that you can. Mathematics 490 – Introduction to Topology Winter 2007 What is this? This is a collection of topology notes compiled by Math 490 topology students at the University of Michigan in the Winter 2007 semester. Introductory topics of point-set and algebraic topology are covered in a series of five chapters. Data Communication and Computer Network 2 All devices connected together with a single device, creating star-like structure. All devices connected arbitrarily using all previous ways to connect each other, resulting in a hybrid structure. Administration From an administrator’s point of view, a network can be private network which.
Alternatively referred to as a line topology, a bus topology is a network setup in which each computer and network device are connected to a single cable or backbone. Depending on the type of network card used in each computer of the bus topology, a coaxial cable or an RJ-45 network cable is used to connect them together.
The following sections contain both the advantages and disadvantages of using a bus topology with your devices.
Advantages of bus topology
- It works well when you have a small network.
- It's the easiest network topology for connecting computers or peripherals in a linear fashion.
- It requires less cable length than a star topology.
Disadvantages of bus topology
- It can be difficult to identify the problems if the whole network goes down.
- It can be hard to troubleshoot individual device issues.
- Bus topology is not great for large networks.
- Terminators are required for both ends of the main cable.
- Additional devices slow the network down.
- If a main cable is damaged, the network fails or splits into two.
Introduction To Topology Pdf

Related pages
- Computer network and network card help and support.
Bus, Network terms, Peripheral, Star topology, Topology
In computer networking, topology refers to the layout of connected devices. This article introduces the standard topologies of networking.
Topology in Network Design
Think of a topology as a network's virtual shape or structure. This shape does not necessarily correspond to the actual physical layout of the devices on the network. For example, the computers on a home network may be arranged in a circle in a family room, but it would be highly unlikely to find a ring topology there.
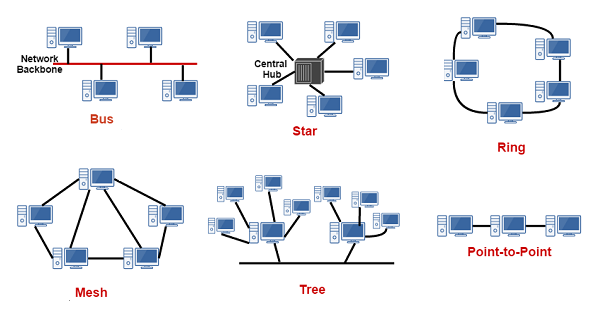
Network topologies are categorized into the following basic types:
- Bus
- Ring
- Star
- Tree
- Mesh
More complex networks can be built as hybrids of two or more of these basic topologies.
Bus Topology
Bus networks (not to be confused with the system bus of a computer) use a common backbone to connect all devices. The backbone is a single cable that functions as a shared communication medium that devices attach or tap into with an interface connector. A device that wants to communicate with another device on the network sends a broadcast message to the wire that the other devices see, but only the intended recipient can accept and process the message.
Ethernet bus topologies are relatively easy to install and don't require much cabling compared to the alternatives. 10Base-2 (ThinNet) and 10Base-5 (ThickNet) were popular Ethernet cabling options for bus topologies. However, bus networks work best with a limited number of devices. If more than a few dozen computers are added to a network bus, performance problems result. In addition, if the backbone cable fails, the network is unusable.
Ring Topology
In a ring network, every device has exactly two neighbors for communication purposes. All messages travel through a ring in the same direction (either clockwise or counterclockwise). A failure in any cable or device breaks the loop and can take down the network.
Ring networks are implemented using FDDI, SONET, or Token Ring technology. Ring topologies are found in office buildings and school campuses.
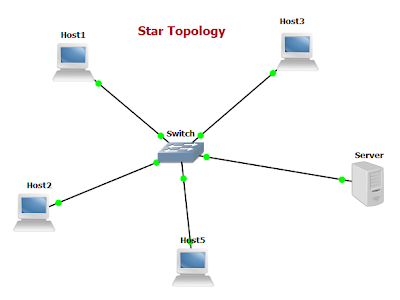
Star Topology
Many home networks use star topology. A star network features a central connection point called a hub node that is either a network hub, switch or router. Devices typically connect to the hub with Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) Ethernet.
Compared to the bus topology, a star network generally requires more cable, but a failure in any star network cable only takes down network access for one computer, not the entire LAN. If the hub fails, however, the entire network fails.
Tree Topology
What Is Topology In Computer Network Pdf
A tree topology joins multiple star topologies together onto a bus. In its simplest form, only hub devices connect to the tree bus, and each hub functions as the root of a tree of devices. This bus/star hybrid approach supports future expansion of the network better than a bus (limited in the number of devices due to the broadcast traffic it generates) or a star (limited by the number of hub connection points).
Mesh Topology
Mesh topology introduces the concept of routes. Unlike the other topologies, messages sent on a mesh network can take any of several possible paths from source to destination. (In a ring, although two cable paths exist, messages only travel in one direction.) Some WANs, most notably the internet, employ mesh routing.
A mesh network in which every device connects to every other is called a full mesh. Partial mesh networks also exist in which some devices connect only indirectly to others.
Summary
What Is Network Topology Pdf
Topology remains an important part of network design theory. It's possible to build a home or small business computer network without understanding the difference between a bus design and a star design, but becoming familiar with the standard topologies provides a better understanding of networking concepts such as hubs, broadcasts, and routes.